
World Obesity Day,Recognizing the obesity problem
4th March is the World Obesity Day designated by the World Health Organization.
Theme in this year is "Everybody Needs to Act"
Obesity prevention and treatment , let’s do it together.
Obesity refers to excessive body fat and/or local increase and abnormal distribution of fat. Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease caused by the combined effects of genetic and environmental factors.
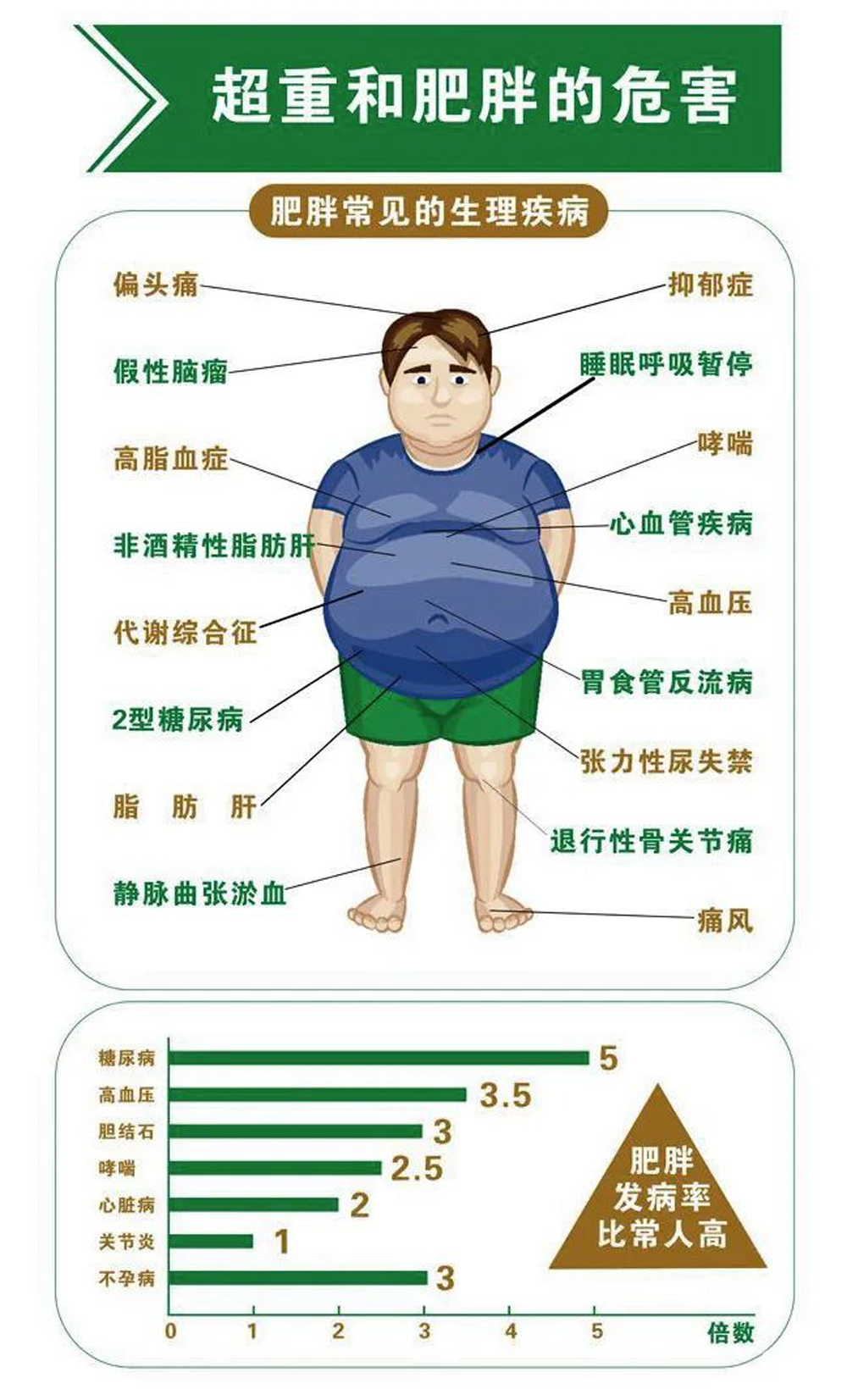
Numerous studies have confirmed that obesity increases people's risk of diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, cancer and other chronic diseases, and shorten patients' life expectancy.

01. Diagnostic standard
BMI is clinically used as a common simple indicator for judging obesity. BMI (kg/m2) = weight (kg)/height2 (m2).

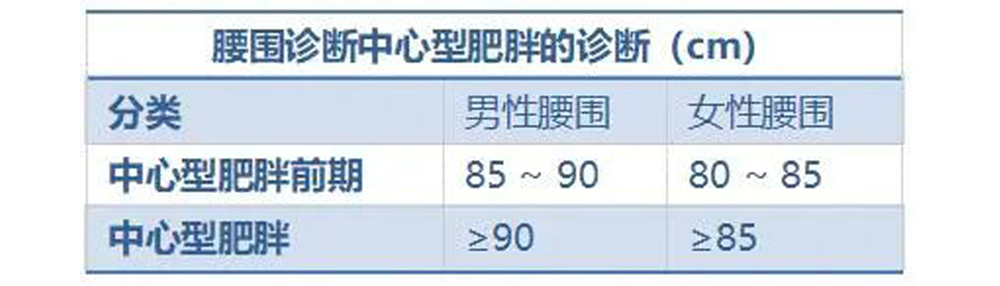
Diagnosis of central obesity by waist circumference
Measurement of waist circumference can diagnose central and peripheral obesity.
The waist circumference measurement method is to take the standing position of the person, and measure the circumference of the mid-axillary line between the lower edge of the costal arch and the midpoint of the iliac crest.
Hip circumference refers to the circumference of the body at the level of the peak of the hip.
A waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) > 1.0 is also known as abdominal obesity.
The more accurate diagnosis of central obesity is to use CT or MRI, select the images of the 4th lumbar vertebra and the 5th lumbar intervertebral layer, and measure the visceral fat area content.
In Chinese population, visceral fat area ≥ 80 cm2 is defined as central obesity.
Diagnosing obesity with body fat percentage
Body fat rate (BFR) refers to the proportion of body fat weight in the total body mass, also known as body fat percentage. Body fat rate measured by bioelectrical impedance method can be used to judge obesity. Body fat percentage > 25% in men and > 30% in women can be considered obese. However, the measurement accuracy of the bioelectrical impedance method is not high, and the measured value is only used as a reference.
02. The dangers of being overweight and obese
A selection of literature related to thromboelastography and obesity
Thromboelastography is a new type of blood viscoelasticity detection system suitable for bedside detection. It uses whole blood samples to monitor the whole process of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis, which can well make up for the shortcomings of traditional coagulation detection.


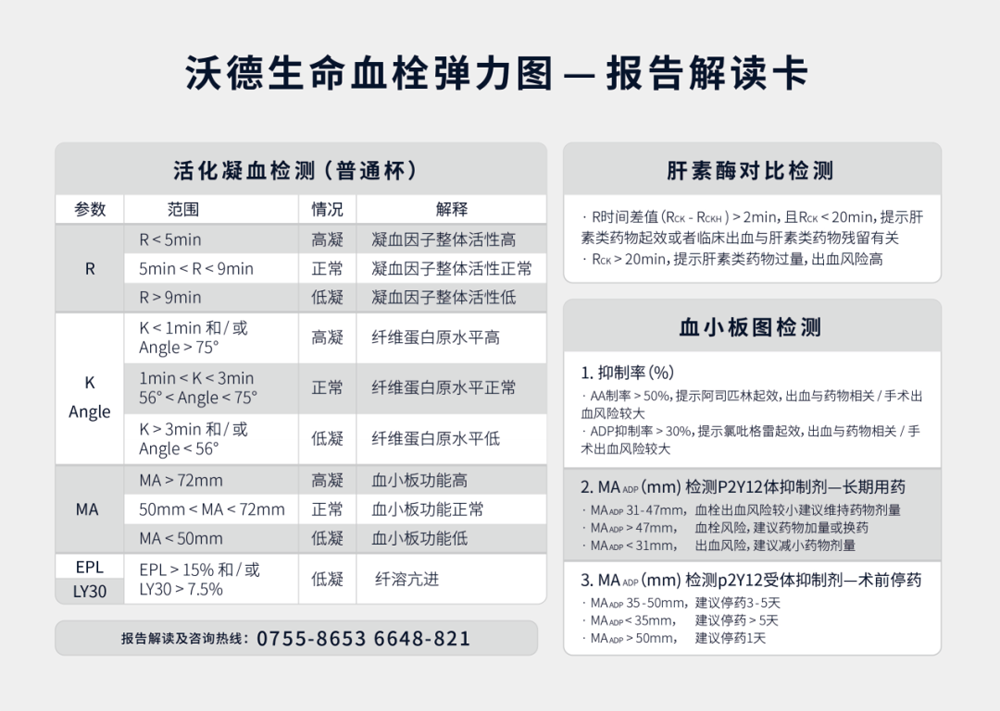
Thromboelastography provides a complete picture of coagulation function. It is a test item that can dynamically monitor the whole process of coagulation and fibrinolysis. It can completely describe the whole process of a blood sample from coagulation initiation - coagulation - dissolution, helping doctors to quickly judge the coagulation state of a patient (high coagulation, low coagulation, hyperfibrinolysis), and analyze its causes. It is of great value for clinical assessment of coagulation function, guidance of component blood transfusion, prediction of thrombosis/bleeding risk, and medication guidance.
01.
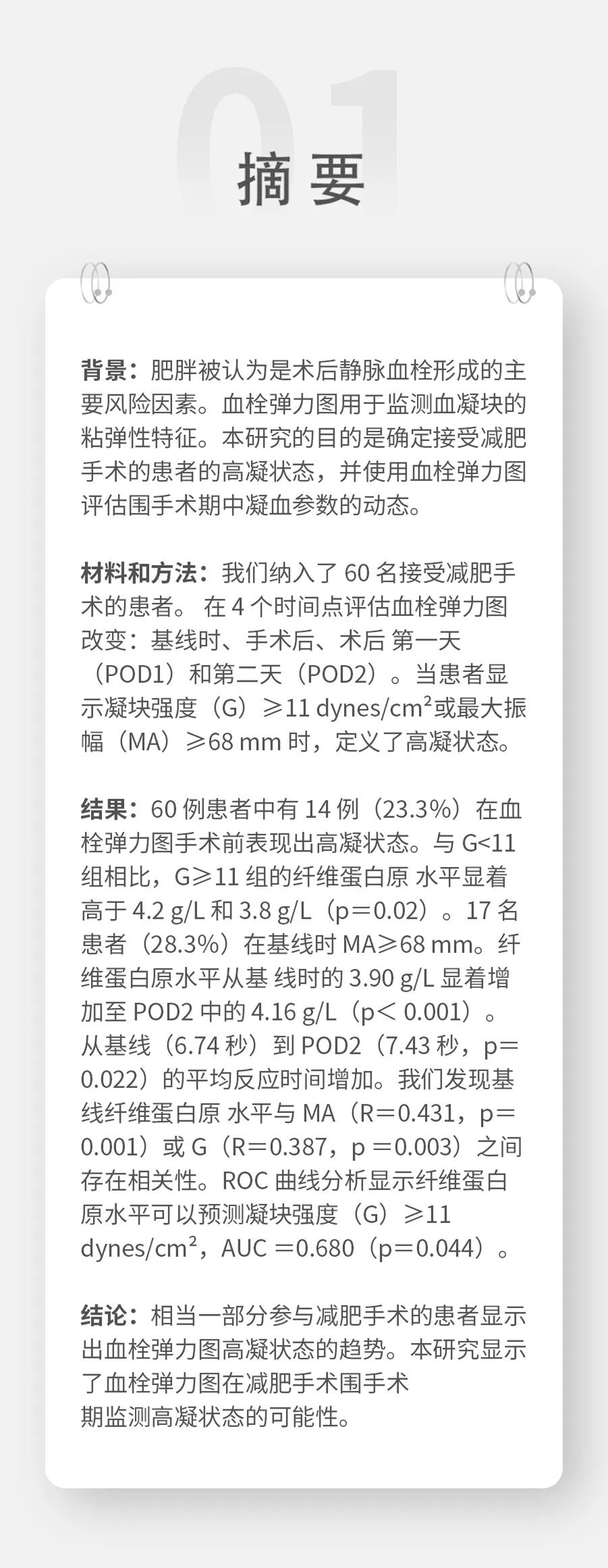
Kupcinskiene K, et al. Monitoring of Hypercoagulability by Thromboelastography in Bariatric Surgery. Med Sci Monit. 2017 Apr 15;23:1819-1826

02.
Moaad F, et al. Is LMWH Sufficient for Anticoagulant Prophylaxis in Bariatric Surgery?
Prospective Study. Obes Surg. 2017 Sep;27(9):2331-2337.


03.
Morgan ES, Wilson E, Melody T, et al. An observational study of haemostatic changes, leptin and soluble endoglin during pregnancy in women with different BMIs. Blood Coagulation & Fibrinolysis, 2017, 28(1): 50-55


04.
Cowling J C, Zhang X, Bajwa K S, et al.Thromboelastography-Based Profiling of Coagulation Status in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery:Analysis of 422 Patients[J]. Obesity Surgery, 2021, 31(8): 3590-3597

Advice on healthy life for obesity:
Lifestyle intervention for obese patients mainly includes three aspects: diet, exercise and habits.

Suggestions for dietary
The principles of healthy eating :
Eat more: whole grains, vegetables, fruits, soybeans and soybeans products, milk and milk products, fish, nuts, water;
Eat less: salty, pickled and smoked foods; high salt; high sugar and sugar-added foods; high-fat and fried foods;
A reasonable weight loss diet should reduce the total daily calorie intake on the basis of dietary nutrient balance. The recommended energy intake for obese men is 1500-1800 kcal/d, and the recommended energy intake for obese women is 1200-1500 kcal/d. Reduce energy intake levels by 500-700 kcal/d.
The energy provided by protein should be less than 15%-20%, carbohydrates , less than 50%-55% and fats less than 30% of the total energy.
Suggestions for sports
Aerobic exercise: It is recommended that overweight or obese people doing moderate-intensity aerobic exercise 60-90 minutes every day, exercise 5-7 days a week.
Resistance exercise: Do resistance muscle strength exercises every other day ,10-20 minutes for one time.
Personalized advice: According to your own health and personal preferences, choose a exercise method and proceed step by step.
Suggestions for changing and forming habits
Record body weight, diet and exercise every day, measure waist and hip circumference regularly;
Avoid sitting for a long time, do not stay up late;
Eat three meals in regular time, control the speed of eating, drink enough water, avoid overeating, reduce eating out, and reduce high-sugar/high-fat/high-salt foods;
Actively seek encouragement and support from family members and social circles;
Receive professional weight loss education and guidance when necessary.

