Coagulation is an important physiological function for the body to maintain the integrity of the blood vessel wall and prevent bleeding.According to statistics, when critically ill patients are admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), the incidence of thrombocytopenia can reach 40.0%-67.6%, and the incidence of international normalized ratio (INR) ≥ 1.5 can exceed 66%.Severe patients with coagulation dysfunction not only have significantly increased bleeding events and need more blood transfusions, but are also more likely to develop multiple organ failure, and their mortality rate is also more than four times higher than that of patients with normal coagulation function.
Early identification of coagulation dysfunction and accurate assessment of coagulation function are the prerequisites and guarantees for correcting coagulation dysfunction as soon as possible. However, at present, there is still a lack of standards for rapid, accurate and standardized assessment of coagulation dysfunction in critically ill patients at home and abroad.

Therefore, the Specialized Committee of Critical Care Medicine of the army and the Specialized Committee of Thrombosis Hemostasis and Critical Illness of the Chinese Medical Education Association jointly formulated the "Chinese Expert Consensus on Standardized Evaluation of Coagulation Dysfunction in Severe Patients".
Recommendations for thromboelastography related tests in the "Consensus":
Recommendation 8: Viscoelasticity test is recommended as a routine diagnostic method for coagulation disorders in critically ill patients (recommendation strength A, evidence level II)
The viscoelastic coagulation test uses whole blood as the test specimen, which can more comprehensively and accurately reflect the coagulation state of patients with coagulation disorders. It is widely recommended in critically ill patients. Therefore, the viscoelastic coagulation test is recommended as a routine tool for evaluating coagulation function in critically ill patients.Viscoelastic coagulation experiments mainly include thromboelastography (thromboelastograph, TEG) and coagulation and platelet function analyzer (Sonoclot@). Both can accurately assess the overall coagulation status of patients, and have a good correlation with the assessment of coagulation factors, fibrinogen and platelet function in critically ill patients. The difference is that the coagulation and platelet function analyzer is more sensitive to the monitoring of coagulation factors and other platelet functions, while TEG has quantitative advantages for the monitoring of fibrinolytic function.
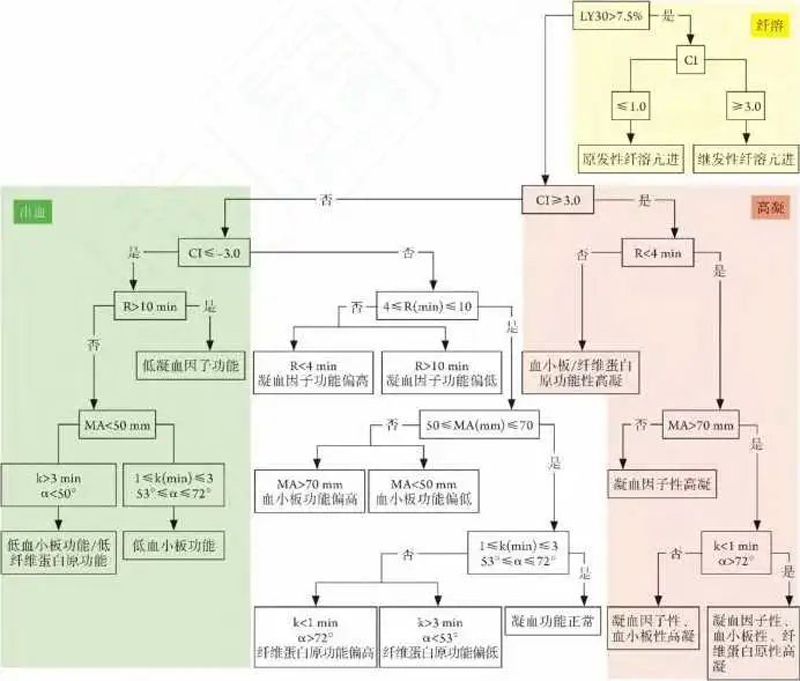
TEG detection can be divided into 5 types of detection types: standard experiment, heparinase comparison experiment, functional fibrinogen (FF) test experiment, rapid detection experiment, and platelet map detection experiment.① TEG general experiment: There are more than 20 indicators, the main indicators are R time (mainly representing blood coagulation factor activity), α angle and k time (mainly representing fibrinogen function), maximum amplitude (maximum amplitude, MA) (mainly representing platelet function) ), solubility (LY30%) at 30 min (mainly representing fibrinolytic function), etc. (Figure 3).② TEG heparinase comparison experiment: carry out TEG general test and heparinase test at the same time, and confirm the presence and strength of heparin from the R time comparison of the two results. For the routine use of unfractionated heparin, the ratio of R normal test/R heparinase test should be 1.5-2.0.③ TEG functional fibrinogen test experiment: adding platelet GP11b/IIla receptor inhibitor, the experimental result removes the effect of platelet. The main indicators of functional fibrinogen test, Rff time, FFma and functional fibrinogen level (FLEV), Rff time reflect the activity of coagulation factors in the extrinsic coagulation pathway, and the normal value is 1.3 to 2.5 minutes. The FFma value is the maximum amplitude, which directly reflects the cross-linking strength of the fibrin network. The normal value is 10.1 to 25.3 mm. The FLEV value reflects the function of fibrinogen activity, and the normal value is 18.43-46.17 mg/L (184.3-461.7 mg/dl).④TEG rapid detection experiment: using tissue factor as an activator to speed up the blood coagulation process, the R time is replaced by activated clotting time (ACT) in terms of parameters, the normal value is 86~118 s, which mainly reflects the activity of extrinsic coagulation pathway factor .⑤TEG platelet graph detection experiment: including the detection of arachidonic acid (AA) and adenine diphosphate (ADP) receptors. The platelet inhibition rate of AA pathway and ADP receptor pathway can be obtained, which can be used to evaluate platelet aggregation function or judge the effect of anti-platelet aggregation drugs. Evaluating the effect of anti-platelet aggregation drugs, the inhibition rate is 50% to 75% to illustrate the onset; if the inhibition rate is too high, the bleeding risk needs to be assessed.